Difference between revisions of "Raspberry Pi and Sensors"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
In this activity, we are going to integrate a HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module Distance Measuring Sensor to measure distance. Modern self-driving cars can use ultrasonic in conjunction with other sensors which may include radar, cameras, GPS and potentially LIDAR. In some cases, ultrasonic sensors can be more reliably that other proximity sensor for detecting movement in an area, such as the presence of a person in a room. | In this activity, we are going to integrate a HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module Distance Measuring Sensor to measure distance. Modern self-driving cars can use ultrasonic in conjunction with other sensors which may include radar, cameras, GPS and potentially LIDAR. In some cases, ultrasonic sensors can be more reliably that other proximity sensor for detecting movement in an area, such as the presence of a person in a room. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note, this activity was designed based on the guide [https://thepihut.com/blogs/raspberry-pi-tutorials/hc-sr04-ultrasonic-range-sensor-on-the-raspberry-pi here] | ||
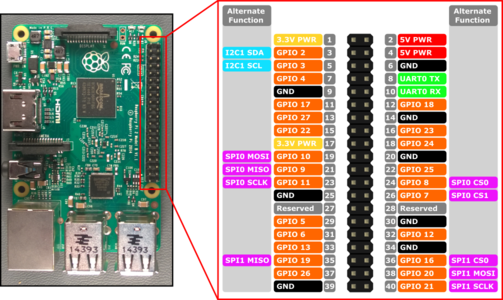
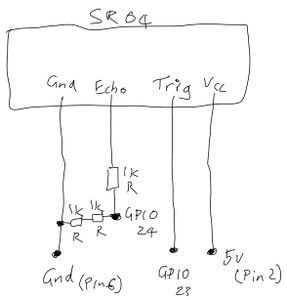
Lets get started by referring to the Raspberry Pi pinout. Then, carefully examine the circuit diagram that we will be using below. | Lets get started by referring to the Raspberry Pi pinout. Then, carefully examine the circuit diagram that we will be using below. | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 19 July 2020
In this activity, we are going to integrate a HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module Distance Measuring Sensor to measure distance. Modern self-driving cars can use ultrasonic in conjunction with other sensors which may include radar, cameras, GPS and potentially LIDAR. In some cases, ultrasonic sensors can be more reliably that other proximity sensor for detecting movement in an area, such as the presence of a person in a room.
Note, this activity was designed based on the guide here
Lets get started by referring to the Raspberry Pi pinout. Then, carefully examine the circuit diagram that we will be using below.
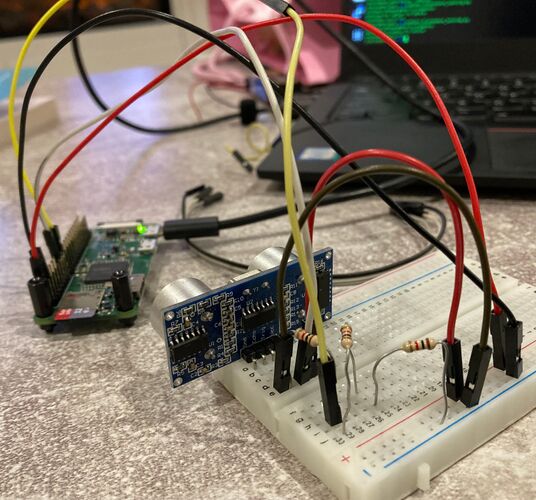
Finally, examine the picture, of my SR04 wired up, below to confirm your understanding. You may want to click on ti to get a high res version. Note that to reduce the number of resistors we were required to purchase, I have used 2 x 1k Resistors rather than a single 1k resistor.
Please read here for a more thorough description of the electronics used in this activity.
#!/usr/bin/python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
TRIG = 23
ECHO = 24
print("Distance Measurement In Progress")
GPIO.setup(TRIG,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(ECHO,GPIO.IN)
GPIO.output(TRIG, False)
print("Waiting For Sensor To Settle")
time.sleep(2)
GPIO.output(TRIG, True)
time.sleep(0.00001)
GPIO.output(TRIG, False)
while GPIO.input(ECHO)==0:
pulse_start = time.time()
while GPIO.input(ECHO)==1:
pulse_end = time.time()
pulse_duration = pulse_end - pulse_start
distance = pulse_duration * 17150
distance = round(distance, 2)
print("Distance:",distance,"cm")
GPIO.cleanup()